Lo studio dei processi di formatura plastica viene eseguito mediante l’approccio sistemico consistente nell’analizzare le relazioni tra i parametri di ingresso e di uscita del processo al fine di ottenere parti esenti da difetti, con elevate proprietà meccaniche. A tal proposito, sono state utilizzate, anche in modo combinato, metodologie sperimentali, codici numerici di calcolo e tecniche di intelligenza artificiale.
In dettaglio, le ricerche riguardano principalmente le seguenti tematiche:
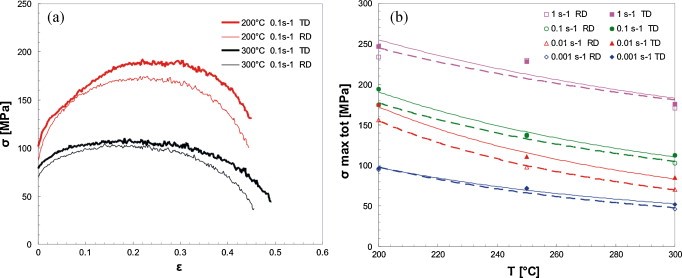
Influence of fibre orientation on the: (a) flow curves and (b) peak stress.
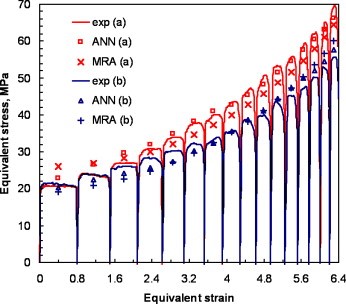
Effect of time between two subsequent deformation steps on the experimental flow curve and predicted envelope curves (T = 525 → 300 °C; ; ɛp = 0.8 → 0.2): (a) tp = 20 s, and (b) tp = 300 s.
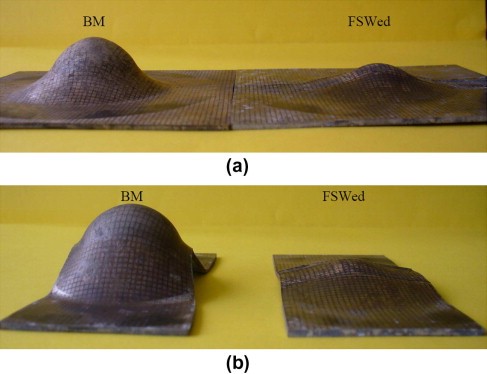
Comparison between BM and FSWed samples, characterised by different width to length ratios, subjected to the hemispherical punch test at 350 °C and 0.1 mm/s: (a) 100 mm × 100 mm; (b) 45 mm × 100 mm.

Billet before and after different forging steps (alloy: AA 6082-W; temperature: 200°C).
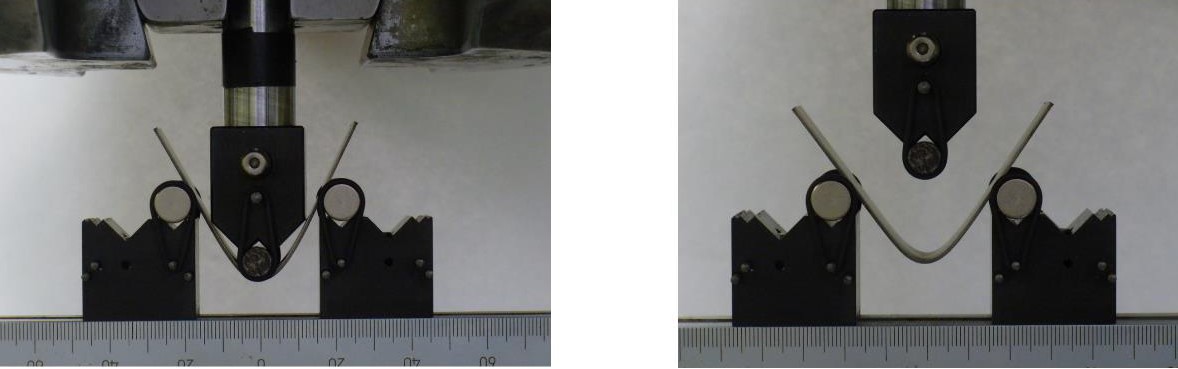
Air bending test for measuring elastic springback of metal sheet
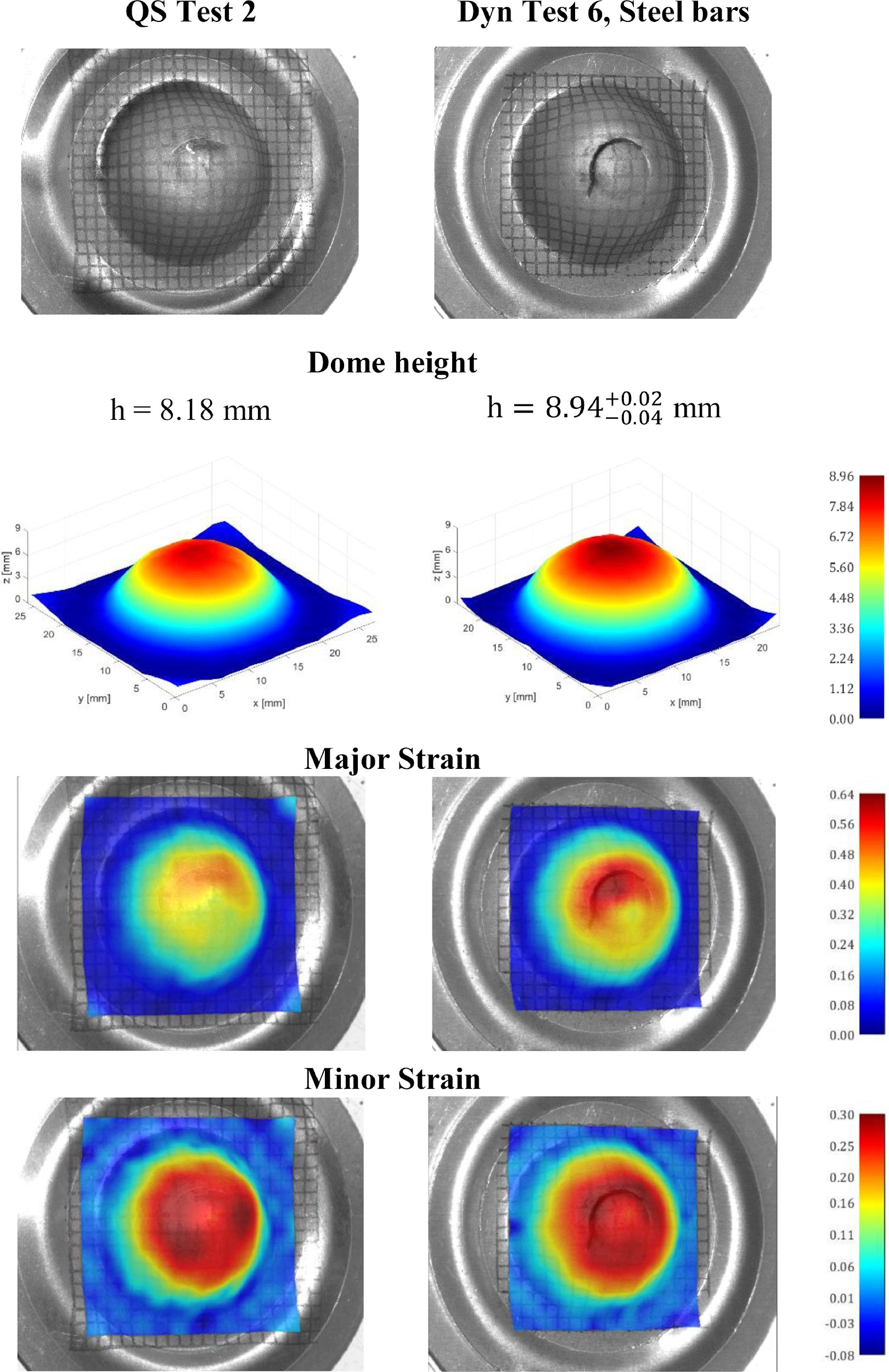
Samples tested at different strain rate up to failure
