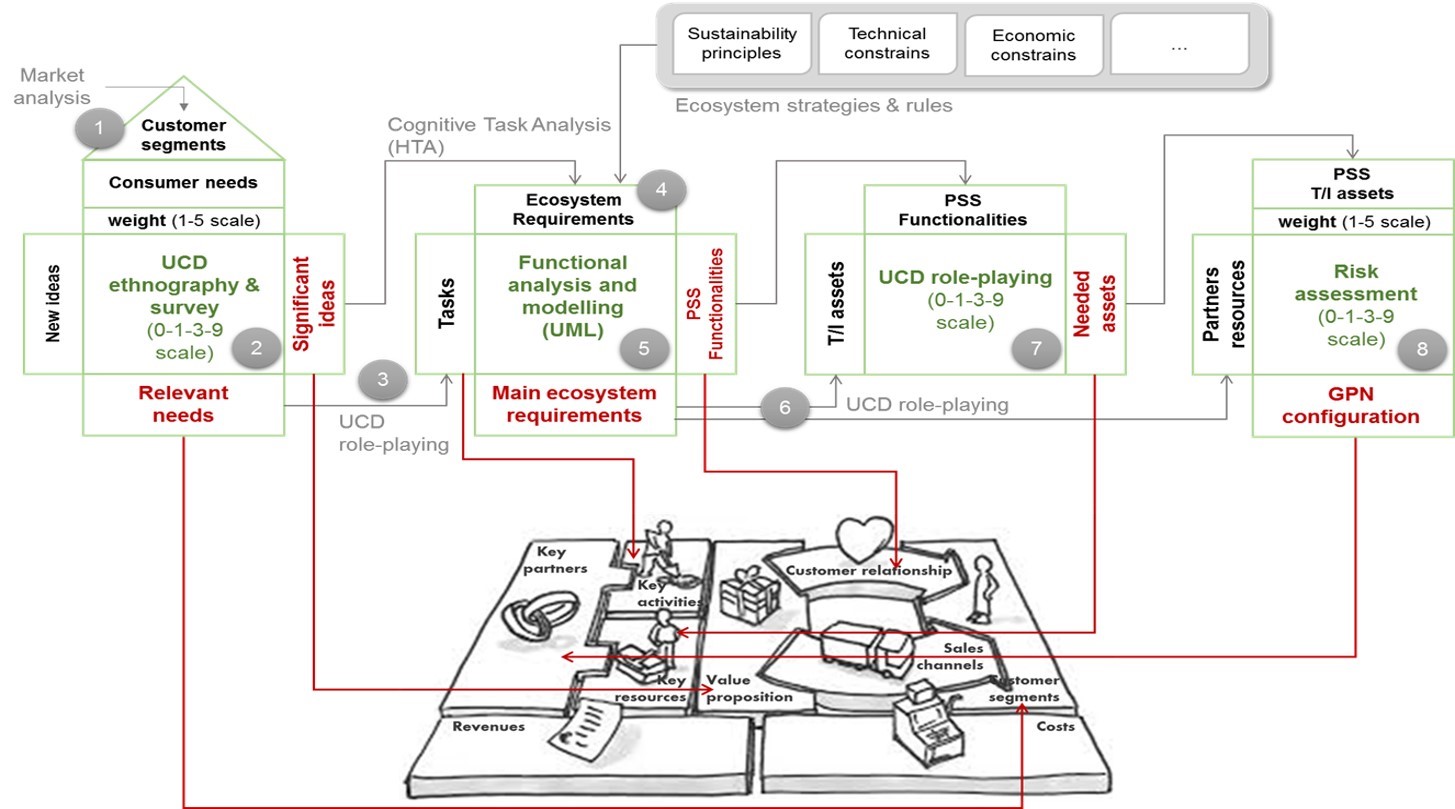
Along the last twenty years, the industrial trend consisting of adding services to the physical product in order to create an added value for customers has concretized, until to see Product Service System (PSS) as a mean to extend the current product lifecycle and therefore, to enhance the company market share. It means offering new usage experiences to the customers, with the aim to sell not the ownership of the products but their usage. Such a trend is becoming a real opportunity for manufacturing industry with the coming of pervasive ICT and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies. However, designing PSSs represents a new challenge for manufacturing companies, because they are involved in the design of no more single products, but a set of integrated and complex systems, providing functions by combining physical devices and intangible assets as well as specific software tools and a proper supporting infrastructure. Companies need to move from a product-oriented to an innovative service-oriented scenario, when a new interpretation of the basic design concepts is adopted and design involves both product and services. For this aim, the research is aimed to propose an innovative approach to support the PSS design in order to extend the current product lifecycle and apply the sustainability concept. In this way, new business models can be generated and defined, already during the PSS design phase. The approach proposed combines several methodologies already exist in literature into a unique and integrated flow able to support the collection and management of information on Product and relative Services along the PSS design process. It goes from the early PSS lifecycle stages (Ideation and Design) until the definition of the production network, the business model definition and the relative sustainability assessment. It provides a strongly user-centered approach during the early stages, to guarantee the satisfaction of the customer needs and the involvement of the most proper partners into the design process. At the same time, each methodology step is also business-centered since business modeling runs in parallel to traditional design activities and effectively supports feasibility analysis and comparison among alternative use scenarios.
Virtual prototyping laboratory
