The studies in this sector, conducted through experimental activities, were carried out with the primary objective of improving the environmental sustainability of the entire system used to carry out machining by chip removal, without neglecting the need to improve the quality of the surfaces worked and the economy of the process.
To this purpose, the focus was on:
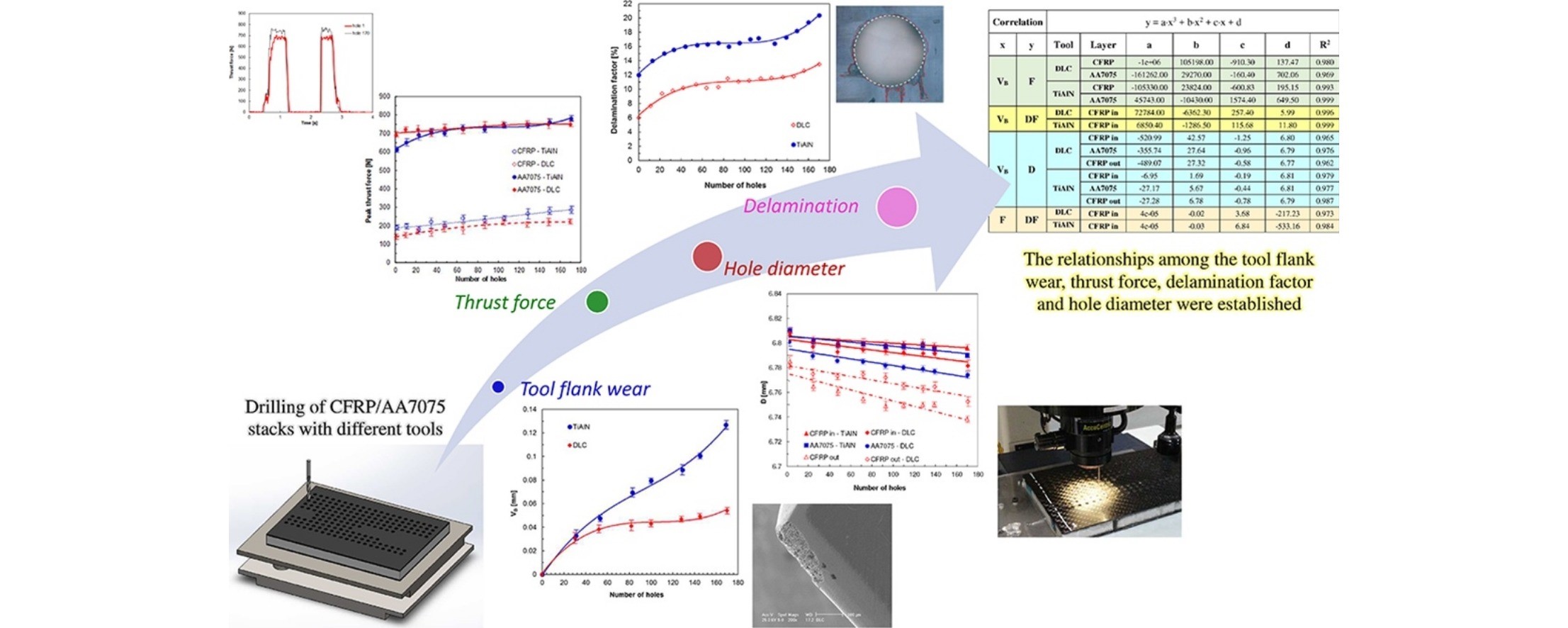
Tool wear and hole quality in drilling of CFRP/AA7075 stacks with DLC and nanocomposite TiAlN coated tools
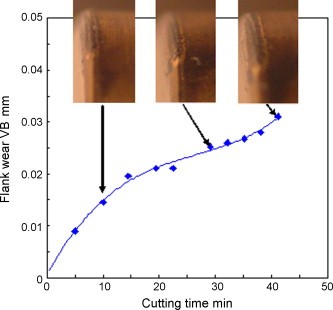
Flank wear vs. cutting time using a PCBN insert, under wet turning condition (polymer concrete bed)
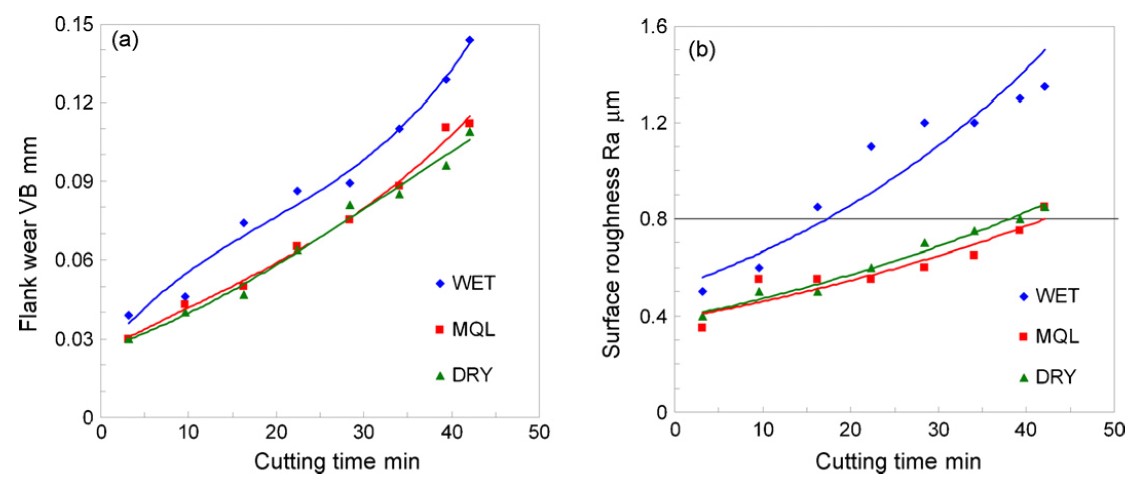
(a) Flank wear vs. cutting time and (b) surface roughness vs. cutting time, under wet, dry and MQL turning conditions, using ceramic inserts (polymer concrete bed).
Laboratories
